About Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers which is rapidly becoming the most fatal cancer worldwide. The occurrence of lung cancer is nearly equal in both men and women. It seems that lung cancer and breast cancer have quite tough competition to rank first in being lethal among women. There is strong evidence that tobacco smoking and other environmental carcinogens are responsible for driving mutations that result in transformation of benign progenitor cells in the lung into neoplastic cells possessing all hallmarks of cancer. Although quitting smoking lowers the risk of lung cancer yet the irreversible damage to the baseline and genetic changes favor the development of lung cancer. Passive smoking is also equally responsible for its development.
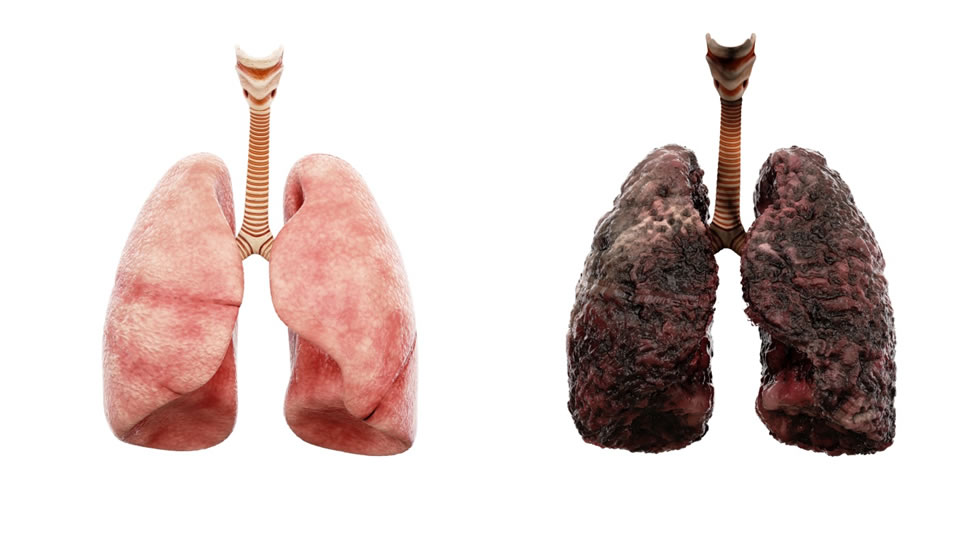
Figure 1: http://waleshealthcare.com/link-blood-pressure-drugs-increased-risk-lung-cancer/
Enough damage to lungs is anticipated before the occurrence of any symptoms. Initially, it is the chronic cough which comes to surface. Hoarseness, chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing and hemoptysis are some other characteristic symptoms. Since lung cancer is usually diagnosed by routine X-Rays and CT scans or when the condition of patient has worsened therefore, symptoms are accompanied with complicated conditions like pleural effusion, pneumonitis, hepatomegaly and pericardial effusion. By the time patient consults a doctor there is high chance the cancer has metastasized presenting conditions like Pancoast syndrome, atelectasis, dysphagia and blurred vision. Weight loss, fatigue, mood changes and headaches are common associations.
According to the microscopic appearance of neoplastic cells, lung cancer is classified into two types;
- Small Cell Lung Cancer is the most aggressive lung cancer and is found only when it has extensively metastasized. It comprises up to 10-15% of all cases. SCLC is commonly caused by cigarette smoking. Medical experts define two stages of SCLC;
- Limited stage, in which the cancer is limited to one lung and the surrounding lymph nodes.
- Extensive stage, in which the cancer spreads throughout the lung, to the opposite lung, to distant organs, to bone marrow, to the fluid surrounding lungs and to the lymph nodes on the opposite lung.
- Non-Small cell Lung Cancer is the most common type of cancer. It comprises up to 85% of total cases. Medical experts define six stages of NCLC;
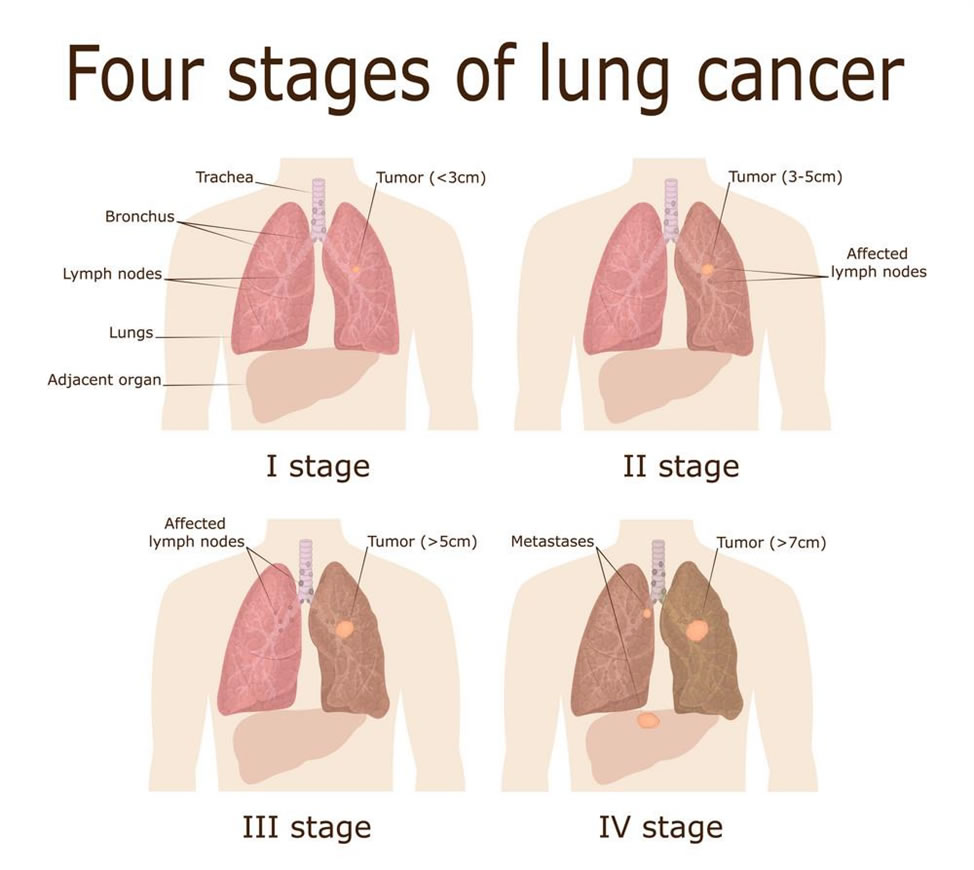
- Hidden, imaging scans does not show cancer but cancerous cells appear in mucus and phlegm.
- Stage 0, cancerous cells are present in the top layers of airway only.
- Stage I, cancer is less than 5 cm in size and doesn’t spread to other areas.
- Stage II, cancer is 5 cm and reaches the lymph nodes around lung or 7 cm in size reaches surrounding tissues but not lymph nodes.
- Stage III, cancer spreads to lungs and lymph nodes of the opposite side as well as above the collarbone.
- Stage IV, cancer spreads extensively and reaches distant organs like brain and bones.
Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Various kinds of surgery include
Wedge resection, to remove only a part of lung which contains tumor.
Segmental resection, to remove slightly big portion of lung but not complete lobe or lung.
Lobectomy, to remove complete lobe of damaged lung.
Pneumonectomy, to remove complete lung.
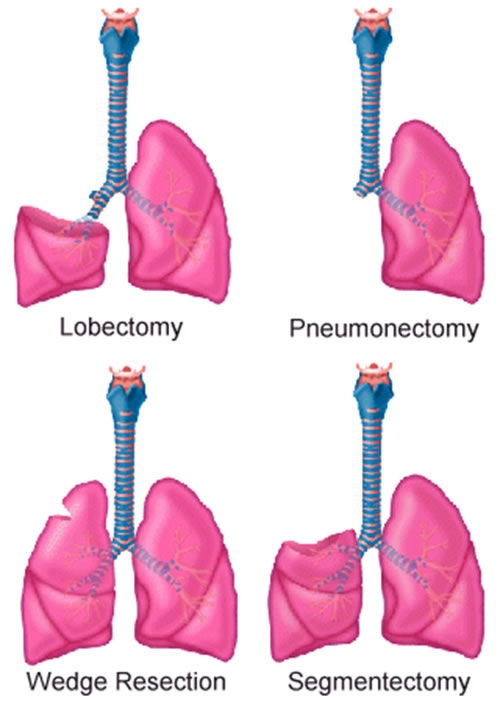
Figure 2: http://www.aboutcancer.com/lung_surgery.htm
To live a healthy life quit smoking now.

FAQs About Lung Cancer
What are the different types of lung cancer? There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC is more common and includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. SCLC is less common but tends to grow and spread more quickly.
How is lung cancer treated? Treatment options depend on the type and stage of lung cancer. They may include surgery to remove the tumor, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy that targets specific genetic mutations, immunotherapy that helps the immune system fight cancer cells, and palliative care to manage symptoms.
Is lung cancer more common in smokers? Yes, smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. The risk of developing lung cancer is significantly higher in smokers compared to non-smokers. Quitting smoking reduces the risk, but former smokers still have a higher risk than those who never smoked.
Can non-smokers get lung cancer? Yes, non-smokers can develop lung cancer. While smoking is the primary cause, exposure to secondhand smoke, environmental pollutants, radon gas, genetic factors, and other unknown factors can also contribute to the development of lung cancer in non-smokers.
What are the early signs of lung cancer? Early signs of lung cancer can include a persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and recurring respiratory infections. However, these symptoms can be similar to other conditions, so it’s important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis.
How is lung cancer diagnosed? Diagnosis usually involves a combination of imaging tests (X-rays, CT scans), biopsies (removal of a tissue sample for examination), and other tests to determine the type, stage, and extent of the cancer.
What is the survival rate for lung cancer? Survival rates vary based on factors like the stage at diagnosis, type of lung cancer, treatment received, and overall health. The 5-year survival rate for lung cancer can range from around 5% for advanced-stage SCLC to over 60% for early-stage NSCLC.
Can lung cancer be prevented? The most effective way to prevent lung cancer is to avoid smoking or quit if you are a smoker. Avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke, reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, and taking safety precautions in workplaces with potential carcinogens can also help lower the risk.
Is lung cancer hereditary? While most cases of lung cancer are linked to smoking and environmental factors, genetics can play a role in susceptibility to the disease. Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of lung cancer, especially in non-smokers.
Are there any promising advancements in lung cancer research? Yes, research into lung cancer continues to advance. Targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and precision medicine approaches are leading to more personalized treatment options. Early detection methods are also being explored to improve survival rates.
Remember that it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate information and advice regarding lung cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Google Reviews
NOVA Pulmonary Critical Care and Sleep Associates is committed to providing excellent care in all aspects of Pulmonary Medicine and Sleep Disorders. With offices located in Lansdowne and Dulles/South Riding, we offer care for the entire Northern Virginia region, serving locations from Chantilly, Fairfax, Centreville, Manassas, Gainesville to Reston, Sterling, Leesburg, Ashburn, Arlington, Brambleton, Purcellville and more.
Office Locations
Conveniently located near you in Loudoun and Fairfax VA
NOVA Pulmonary – Dulles
24430 Stone Springs Boulevard
Suite 200
Dulles, VA 20166
NOVA Pulmonary – Lansdowne
19415 Deerfield Avenue
Suite 301
Landsdowne, VA 20176
